当使用基本数据类型声明变量时,C编译器会自动在称为栈(Stack)的内存池中为变量分配内存空间。
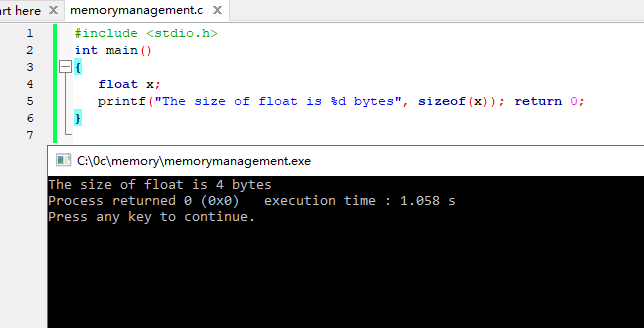
例如,一个float变量在声明时通常占用4个字节(根据平台)。 我们可以使用sizeof运算符验证此信息,如下例所示:
1 2 3 4 5 6 | #include <stdio.h>int main() { float x; printf("The size of float is %d bytes", sizeof(x)); return 0;} |
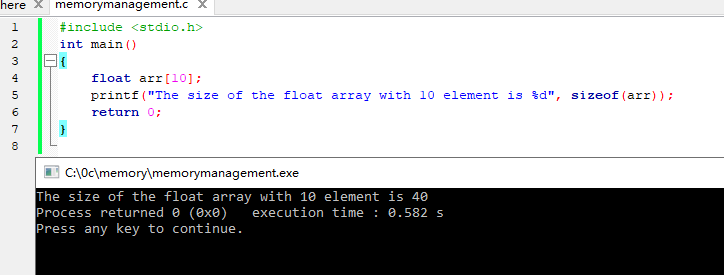
同样,将具有指定大小的数组分配到连续的内存块中,每个块具有一个元素的大小:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 | #include <stdio.h>int main(){ float arr[10]; printf("The size of the float array with 10 element is %d", sizeof(arr)); return 0;} |